论文链接Observe and Look Further, Achieving Consistent Performance on Atari
概要
问题
作者提出了强化学习三个重要问题
- 处理不同的reward分布
- 考虑长期回报
- 高效探索
新方法
针对reward分布的问题,作者提出了一个新的Bellman算子来处理不同分布的reward。
针对第二个问题作者提出了temporal consistency loss,使得我们可以使用更大的折扣率$\gamma = 0.999$.
对于最后一个问题,作者通过在算法中通过结合human demonstrations来引导agent朝reward更大的方向探索。
算法
本文提出的算法结合了针对这三个方向的改进,将loss分为三个部分$L_{TD},L_{TC},L_{IM}$,总loss为这三部分之和。
\[L(\theta;(t_i)^N_{i=1},(p_i)^N_{i=1},\theta^{(k-1)}) = (L_{TD}+L_{TC}+L_{IM})(\theta;(t_i)^N_{i=1},(p_i)^N_{i=1},\theta^{(k-1)})\]Transformed Bellman Operator
作者提出一个新的Bellman算子${\mathcal{T}}_h$
\[({\mathcal{T}}_hQ):=E_{x'~P(·|x,a)}[h(R(x,a)+\gamma\max_{a' \in \mathcal{A}}h^{-1}(Q(x',a')))]\]并证明了当h是严格单调增函数时,对于确定的MDP可以收敛到$h\circ Q^*$
其中,作者使用了$h(z) = sign(z)(\sqrt{|z|+1}-1)+\epsilon z, \space \epsilon=10^{-2}$,末尾的正则项$\epsilon z$用于保证$h^{-1}$是Lipschitz连续的(证明在论文附录中)。
这个算子压缩了Q的范围,使得算法对于不同reward分布更加稳定。
根据这个算子得到的TD error为
\[L_{TD}(\theta;(t_i)^N_{i=1},(p_i)^N_{i=1},\theta^{(k-1)})\] \[= \mathbb{E}_{x,a}[\mathcal{L}(f_\theta(x,a)-(\mathcal{T}_hf_{\theta^{(k-1)}})(x,a))]\] \[= \Sigma_{i=1}^Np_i\mathcal{L}(f_\theta(x_i,a_i)-h(r'_i+\gamma \max_{a' \in \mathcal{A}}h^{-1}(f_{\theta^{(k-1)}}(x'_i,a'_i))))\]The temporal consistency (TC) loss
尽管通过Transformed Bellman Operator压缩了target的范围和方差,但当$\gamma$接近1时target值仍然很不稳定。
Increasing the discount factor decreases the temporal difference in value between non-rewarding states.
作者认为较大的$\gamma$会使得没有直接reward的状态的TD-error被弱化(因为过多的考虑了后续状态的收益)。另外由于前后状态往往是相似的,在更新前一状态时后续状态会受到类似的影响,这也弱化了前后状态的TD-error。于是作者通过增加temporal consistency loss来处理惩罚每次更新对后续状态的影响。
\[L_{TC}(\theta;(t_i)^N_{i=1},(p_i)^N_{i=1},\theta^{(k-1)})\] \[= \Sigma^N_{i=1}p_i\mathcal{L}(f_\theta(x'_i,a'_i)-f_{\theta^{k-1}}(x'_i,a'_i))\]其中
\[a'_i = argmax_{a \in \mathcal{A}} f_\theta(x'_i, a)\]Combining Ape-X DQN and DQfD
作者通过结合DQfD算法,使用Demonstration来引导agent探索到有更高reward的状态。
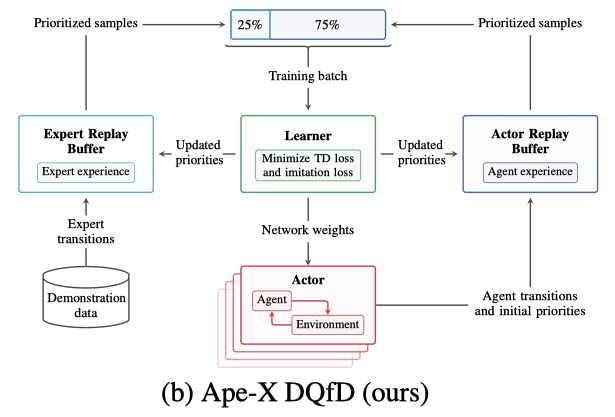
训练上结合了Deep Q-Learnning from Demonstrations论文中的方式,从expert和actor的replay buffer中分别采样用于训练,使用了其中提出的max margin loss来让expert的Q值最高,在本文中称为imitations loss。
\[L_{IM}(\theta;(t_i)^N_{i=1},(p_i)^N_{i=1},\theta^{(k-1)})\] \[\Sigma^N_{i=1}p_ie_i(max_{a \in \mathcal{A}}[f_\theta(x_i,a)+\lambda \delta_{a\not= a_i}]-f_\theta(x_i,a_i))\]分析
本算法在大多数游戏中都取得了更好的效果,并且是第一个在MONTEZUMA’S REVENGE环境(一个奖励非常稀疏的算法)中通关第一层的算法。 但在seaquest中却不如不使用demostration的agent。作者得出结论:由expert data引入的bias在部分游戏中可能是有害的。