论文链接Noisy Networks for Exploration
概要
本文指出强化学习中常用的$\epsilon$-greedy探索方式不够高效,并提出了Noisy Network的方式,通过对网络增加噪声扰动来达到探索的目的。
算法
作者对神经网络的全连接层进行了改造,在weight与bias上增加了噪声以及噪声系数。 普通的全连接层可以表示:
\[y=wx+b\]在增加noise后,改变为:
\[y =^{def} (\mu^w+\sigma^w\odot\epsilon^w)x+\mu^b+\sigma^b\odot\epsilon^b\]$\odot$表示矩阵对应位元素相乘。
对于有p个输入,q个输出的层:
$\mu^w,\sigma^w, \epsilon^w \in \mathbb{R}^{p*q}$,$\mu^b,\sigma^b,\epsilon^b \in \mathbb{R}^q$,其中$\mu^w,\sigma^w,\mu^b,\sigma^b$是可以学习的参数,$\epsilon^w,\epsilon^b$是噪声随机变量。
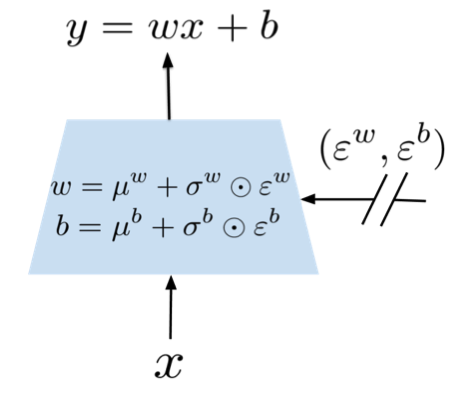
在噪声的设置方面,作者选择使噪声服从高斯分布,并提出了两种采样噪声的方法。
- 独立高斯噪声
这是一种最简单的方式,即所有噪声从独立的高斯分布中采样。
- 分解高斯采样
出于提高产生随机数速度的目的,这种方式在采样$\epsilon^w$时,不从$p*q$个高斯分布中去单独采样,而是从$p+q$个分布中采样出$\epsilon_i\in\mathbb{R}^p,\epsilon_j\in\mathbb{R}^q$,再计算出 $\epsilon^w=f(\epsilon_i)f(\epsilon_j)^T$ 其中$f(x)=sgn(x)\sqrt{|{x}|}$。
论文中提到为了保证weight与bias中output noise相同,所以令 $\epsilon^b$也等于$f(\epsilon_j)$而非直接使用$\epsilon_j$。
效果
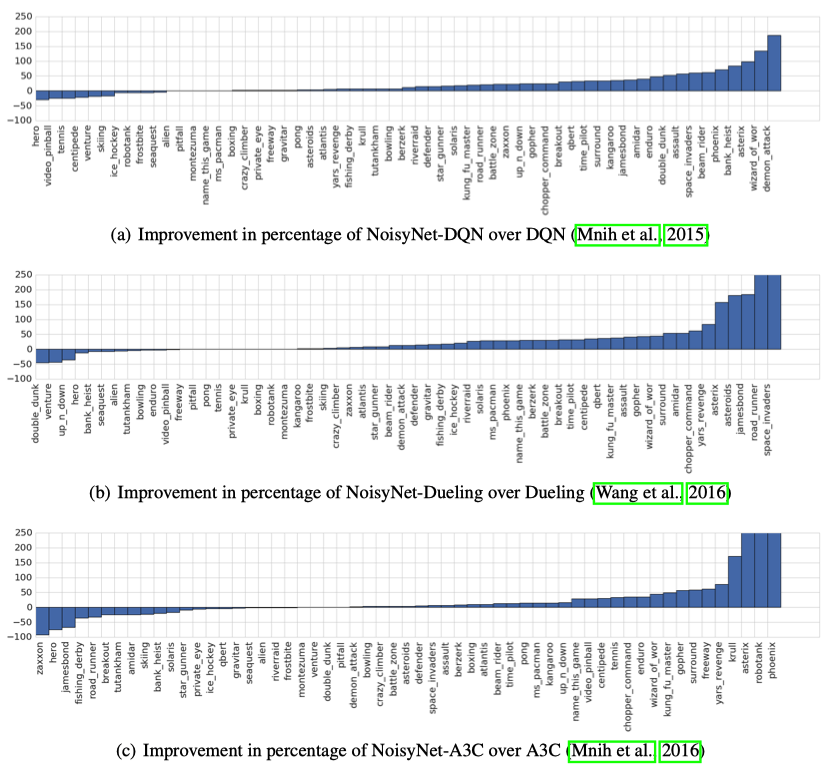
作者对比了使用$\epsilon$-greedy方式和使用NoisyNet的DQN,DuelingDQN,还对比了通过增加Entropy惩罚项来鼓励探索和不使用Entropy项而改用NoisyNet的A3C算法。NoisyNet在大部分atari游戏上取得了更好的结果。
核心功能代码
本算法的核心功能是对全连接层的改造,通过创建基于NoisyNetwork的全连接层来创建神经网络,即可运用到各种强化学习算法中去。 pytorch代码示例如下。注意使用nn.Parameter和register_buffer来声明需要训练和不需要训练的tensor。
class NoisyLinear(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_features, out_features, std_init=0.5, factorised=False):
super(NoisyLinear, self).__init__()
self.in_features = in_features
self.out_features = out_features
self.std_init = std_init
self.factorised = factorised
self.weight_mu = nn.Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(out_features, in_features))
self.weight_sigma = nn.Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(out_features, in_features))
self.register_buffer('weight_epsilon', torch.FloatTensor(out_features, in_features))
self.bias_mu = nn.Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(out_features))
self.bias_sigma = nn.Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(out_features))
self.register_buffer('bias_epsilon', torch.FloatTensor(out_features))
self.reset_parameters()
self.reset_noise()
def forward(self, x):
if self.training:
weight = self.weight_mu + self.weight_sigma.mul(self.weight_epsilon)
bias = self.bias_mu + self.bias_sigma.mul(self.bias_epsilon)
else:
weight = self.weight_mu
bias = self.bias_mu
return F.linear(x, weight, bias)
def reset_parameters(self):
mu_range = math.sqrt(3/self.in_features) if self.factorised else math.sqrt(1/self.in_features)
theta = 0.017 if self.factorised else self.std_init/math.sqrt(self.in_features)
self.weight_mu.data.uniform_(-mu_range, mu_range)
self.weight_sigma.data.fill_(theta)
self.bias_mu.data.uniform_(-mu_range, mu_range)
self.bias_sigma.data.fill_(theta)
def reset_noise(self):
if self.factorised:
epsilon_in = self._scale_noise(self.in_features)
epsilon_out = self._scale_noise(self.out_features)
self.weight_epsilon.copy_(epsilon_out.ger(epsilon_in))
self.bias_epsilon.copy_(epsilon_out)
else:
self.weight_epsilon.copy_(torch.randn((self.out_features, self.in_features)))
self.bias_epsilon.copy_(torch.randn(self.out_features))
def _scale_noise(self, size):
x = torch.randn(size)
x = x.sign().mul(x.abs().sqrt())
return x